[ Main Table Of Contents | Table Of Contents | Keyword Index | Categories | Modules | Applications ]
pt::rde(n) 1.1 tcllib "Parser Tools"
Name
pt::rde - Parsing Runtime Support, PARAM based
Synopsis
- package require Tcl 8.5
- package require pt::rde ?1.1?
- package require snit
- package require struct::stack 1.5
- package require pt::ast 1.1
- ::pt::rde objectName
- objectName destroy
- objectName reset chan
- objectName complete
- objectName chan
- objectName line
- objectName column
- objectName current
- objectName location
- objectName locations
- objectName ok
- objectName value
- objectName error
- objectName errors
- objectName tokens ?from ?to??
- objectName symbols
- objectName known
- objectName reducible
- objectName asts
- objectName ast
- objectName position loc
- objectName i_input_next msg
- objectName i_test_alnum
- objectName i_test_alpha
- objectName i_test_ascii
- objectName i_test_char char
- objectName i_test_ddigit
- objectName i_test_digit
- objectName i_test_graph
- objectName i_test_lower
- objectName i_test_print
- objectName i_test_punct
- objectName i_test_range chars chare
- objectName i_test_space
- objectName i_test_upper
- objectName i_test_wordchar
- objectName i_test_xdigit
- objectName i_error_clear
- objectName i_error_push
- objectName i_error_pop_merge
- objectName i_error_nonterminal symbol
- objectName i_status_ok
- objectName i_status_fail
- objectName i_status_negate
- objectName i_loc_push
- objectName i_loc_pop_discard
- objectName i_loc_pop_rewind
- objectName i:ok_loc_pop_rewind
- objectName i_loc_pop_rewind/discard
- objectName i_symbol_restore symbol
- objectName i_symbol_save symbol
- objectName i_value_clear
- objectName i_value_clear/leaf
- objectName i_value_clear/reduce
- objectName i:ok_ast_value_push
- objectName i_ast_push
- objectName i_ast_pop_rewind
- objectName i:fail_ast_pop_rewind
- objectName i_ast_pop_rewind/discard
- objectName i_ast_pop_discard
- objectName i_ast_pop_discard/rewind
- objectName i:ok_continue
- objectName i:fail_continue
- objectName i:fail_return
- objectName i:ok_return
- objectName si:void_state_push
- objectName si:void2_state_push
- objectName si:value_state_push
- objectName si:void_state_merge
- objectName si:void_state_merge_ok
- objectName si:value_state_merge
- objectName si:value_notahead_start
- objectName si:void_notahead_exit
- objectName si:value_notahead_exit
- objectName si:kleene_abort
- objectName si:kleene_close
- objectName si:voidvoid_branch
- objectName si:voidvalue_branch
- objectName si:valuevoid_branch
- objectName si:valuevalue_branch
- objectName si:voidvoid_part
- objectName si:voidvalue_part
- objectName si:valuevalue_part
- objectName si:value_symbol_start symbol
- objectName si:value_void_symbol_start symbol
- objectName si:void_symbol_start symbol
- objectName si:void_void_symbol_start symbol
- objectName si:reduce_symbol_end symbol
- objectName si:void_leaf_symbol_end symbol
- objectName si:value_leaf_symbol_end symbol
- objectName si:value_clear_symbol_end symbol
- objectName si:void_clear_symbol_end symbol
- objectName si:next_char tok
- objectName si:next_range toks toke
- objectName si:next_alnum
- objectName si:next_alpha
- objectName si:next_ascii
- objectName si:next_ddigit
- objectName si:next_digit
- objectName si:next_graph
- objectName si:next_lower
- objectName si:next_print
- objectName si:next_punct
- objectName si:next_space
- objectName si:next_upper
- objectName si:next_wordchar
- objectName si:next_xdigit
Description
Are you lost ? Do you have trouble understanding this document ? In that case please read the overview provided by the Introduction to Parser Tools. This document is the entrypoint to the whole system the current package is a part of.
This package provides a class whose instances provide the runtime support for recursive descent parsers with backtracking, as is needed for the execution of, for example, parsing expression grammars. It implements the PackRat Machine Specification, as such that document is required reading to understand both this manpage, and the package itself. The description below does make numerous shorthand references to the PARAM's instructions and the various parts of its architectural state.
The package resides in the Execution section of the Core Layer of Parser Tools.
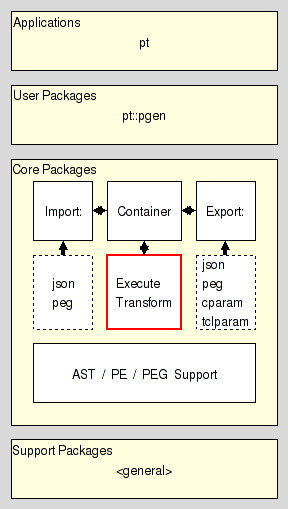
Note: This package not only has the standard Tcl implementation, but also an accelerator, i.e. a C implementation, based on Critcl.
Class API
The package exports the API described here.
- ::pt::rde objectName
The command creates a new runtime object for a recursive descent parser with backtracking and returns the fully qualified name of the object command as its result. The API of this object command is described in the section Object API. It may be used to invoke various operations on the object.
Object API
All objects created by this package provide the following 63 methods for the manipulation and querying of their state, which is, in essence the architectural state of a PARAM.
First some general methods and the state accessors.
- objectName destroy
This method destroys the object, releasing all claimed memory, and deleting the associated object command.
- objectName reset chan
This method resets the state of the runtme to its defaults, preparing it for the parsing of the character in the channel chan, which becomes IN.
Note here that the Parser Tools are based on Tcl 8.5+. In other words, the channel argument is not restricted to files, sockets, etc. We have the full power of reflected channels available.
It should also be noted that the parser pulls the characters from the input stream as it needs them. If a parser created by this package has to be operated in a push aka event-driven manner it will be necessary to go to Tcl 8.6+ and use the coroutine::auto to wrap it into a coroutine where read is properly changed for push-operation.
- objectName complete
This method completes parsing, either returning the AST made from the elements of ARS, or throwing an error containing the current ER.
- objectName chan
This method returns the handle of the channel which is IN.
- objectName line
This method returns the line number for the position IN is currently at. Note that this may not match with the line number for CL, due to backtracking.
- objectName column
This method returns the column for the position IN is currently at. Note that this may not match with the column for CL, due to backtracking.
- objectName current
This method returns CC.
- objectName location
This method returns CL.
- objectName locations
This method returns the LS. The topmost entry of the stack will be the first element of the returned list.
- objectName ok
This method returns ST.
- objectName value
This method returns SV.
- objectName error
This method returns ER. This is either the empty string for an empty ER, or a list of 2 elements, the location the error is for, and a set of messages which specify which symbols were expected at the location. The messages are encoded as one of the possible atomic parsing expressions (special operators, terminal, range, and nonterminal operator).
- objectName errors
This method returns ES. The topmost entry of the stack will be the first element of the returned list. Each entry is encoded as described for error.
- objectName tokens ?from ?to??
This method returns the part of TC for the range of locations of IN starting at from and ending at to. If to is not specified it is taken as identical to from. If neither argument is specified the whole of TC is returned.
Each token in the returned list is a list of three elements itself, containing the character at the location, and the associated line and column numbers, in this order.
- objectName symbols
This method returns a dictionary containing NC. Keys are two-element lists containing nonterminal symbol and location, in this order. The values are 4-tuples containing CL, ST, ER, and SV, in this order. ER is encoded as specified for the method error.
- objectName known
This method returns a list containing the keys of SC. They are encoded in the same manner as is done by method symbols.
- objectName reducible
This method returns ARS. The topmost entry of the stack will be the first element of the returned list
- objectName asts
This method returns AS. The topmost entry of the stack will be the first element of the returned list
- objectName ast
This is a convenience method returning the topmost element of ARS.
- objectName position loc
This method returns the line and column numbers for the specified location of IN, assuming that this location has already been reached during the parsing process.
The following methods implement all PARAM instructions. They all have the prefix "i_".
The control flow is mainly provided by Tcl's builtin commands, like if, while, etc., plus a few guarded variants of PARAM instructions and Tcl commands.. That means that these instruction variants will do nothing if their guard condition is not fulfilled. They can be recognized by the prefix "i:ok_" and "i:fail_", which denote the value ST has to have for the instruction to execute.
The instructions are listed in the same order they occur in the PackRat Machine Specification, with the guard variants listed after their regular implementation, if any, or in their place.
- objectName i_input_next msg
This method implements the PARAM instruction input_next.
- objectName i_test_alnum
This method implements the PARAM instruction test_alnum.
- objectName i_test_alpha
This method implements the PARAM instruction test_alpha.
- objectName i_test_ascii
This method implements the PARAM instruction test_ascii.
- objectName i_test_char char
This method implements the PARAM instruction test_char.
- objectName i_test_ddigit
This method implements the PARAM instruction test_ddigit.
- objectName i_test_digit
This method implements the PARAM instruction test_digit.
- objectName i_test_graph
This method implements the PARAM instruction test_graph.
- objectName i_test_lower
This method implements the PARAM instruction test_lower.
- objectName i_test_print
This method implements the PARAM instruction test_print.
- objectName i_test_punct
This method implements the PARAM instruction test_punct.
- objectName i_test_range chars chare
This method implements the PARAM instruction test_range.
- objectName i_test_space
This method implements the PARAM instruction test_space.
- objectName i_test_upper
This method implements the PARAM instruction test_upper.
- objectName i_test_wordchar
This method implements the PARAM instruction test_wordchar.
- objectName i_test_xdigit
This method implements the PARAM instruction test_xdigit.
- objectName i_error_clear
This method implements the PARAM instruction error_clear.
- objectName i_error_push
This method implements the PARAM instruction error_push.
- objectName i_error_pop_merge
This method implements the PARAM instruction error_pop_merge.
- objectName i_error_nonterminal symbol
This method implements the PARAM instruction error_nonterminal.
- objectName i_status_ok
This method implements the PARAM instruction status_ok.
- objectName i_status_fail
This method implements the PARAM instruction status_fail.
- objectName i_status_negate
This method implements the PARAM instruction status_negate.
- objectName i_loc_push
This method implements the PARAM instruction loc_push.
- objectName i_loc_pop_discard
This method implements the PARAM instruction loc_pop_discard.
- objectName i_loc_pop_rewind
This method implements the PARAM instruction loc_pop_rewind.
- objectName i:ok_loc_pop_rewind
This guarded method, a variant of i_loc_pop_rewind, executes only for "ST == ok".
- objectName i_loc_pop_rewind/discard
This method is a convenient combination of control flow and the two PARAM instructions loc_pop_rewind and loc_pop_discard. The former is executed for "ST == fail", the latter for "ST == ok".
- objectName i_symbol_restore symbol
This method implements the PARAM instruction symbol_restore.
The boolean result of the check is returned as the result of the method and can be used with standard Tcl control flow commands.
- objectName i_symbol_save symbol
This method implements the PARAM instruction symbol_save.
- objectName i_value_clear
This method implements the PARAM instruction value_clear.
- objectName i_value_clear/leaf
This method is a convenient combination of control flow and the two PARAM instructions value_clear and value_leaf. The former is executed for "ST == fail", the latter for "ST == ok".
- objectName i_value_clear/reduce
This method is a convenient combination of control flow and the two PARAM instructions value_clear and value_reduce. The former is executed for "ST == fail", the latter for "ST == ok".
- objectName i:ok_ast_value_push
This method implements a guarded variant of the the PARAM instruction ast_value_push, which executes only for "ST == ok".
- objectName i_ast_push
This method implements the PARAM instruction ast_push.
- objectName i_ast_pop_rewind
This method implements the PARAM instruction ast_pop_rewind.
- objectName i:fail_ast_pop_rewind
This guarded method, a variant of i_ast_pop_rewind, executes only for "ST == fail".
- objectName i_ast_pop_rewind/discard
This method is a convenient combination of control flow and the two PARAM instructions ast_pop_rewind and ast_pop_discard. The former is executed for "ST == fail", the latter for "ST == ok".
- objectName i_ast_pop_discard
This method implements the PARAM instruction ast_pop_discard.
- objectName i_ast_pop_discard/rewind
This method is a convenient combination of control flow and the two PARAM instructions ast_pop_discard and ast_pop_rewind. The former is executed for "ST == fail", the latter for "ST == ok".
- objectName i:ok_continue
This guarded method executes only for "ST == ok". Then it aborts the current iteration of the innermost loop in the calling Tcl procedure.
- objectName i:fail_continue
This guarded method executes only for "ST == fail". Then it aborts the current iteration of the innermost loop in the calling Tcl procedure.
- objectName i:fail_return
This guarded method executes only for "ST == fail". Then it aborts the calling Tcl procedure.
- objectName i:ok_return
This guarded method executes only for "ST == ok". Then it aborts the calling Tcl procedure.
The next set of methods are super instructions, meaning that each implements a longer sequence of instructions commonly used in parsers. The combinated instructions of the previous set, i.e. those with names matching the pattern "i_*/*", are actually super instructions as well, albeit with limited scope, handling 2 instructions with their control flow. The upcoming set is much broader in scope, folding as much as six or more PARAM instructions into a single method call.
In this we can see the reasoning behind their use well:
By using less instructions the generated parsers become smaller, as the common parts are now truly part of the common runtime, and not explicitly written in the parser's code over and over again.
Using less instructions additionally reduces the overhead associated with calls into the runtime, i.e. the cost of method dispatch and of setting up the variable context.
Another effect of the super instructions is that their internals can be optimized as well, especially regarding control flow, and stack use, as the runtime internals are accessible to all instructions folded into the sequence.
- objectName si:void_state_push
This method combines
i_loc_push i_error_clear i_error_push
Parsers use it at the beginning of void sequences and choices with a void initial branch.
- objectName si:void2_state_push
This method combines
i_loc_push i_error_clear i_error_push
Parsers use it at the beginning of optional and repeated expressions.
- objectName si:value_state_push
This method combines
i_ast_push i_loc_push i_error_clear i_error_push
Parsers use it at the beginning of sequences generating an AST and choices with an initial branch generating an AST.
- objectName si:void_state_merge
This method combines
i_error_pop_merge i_loc_pop_rewind/discard
Parsers use it at the end of void sequences and choices whose last branch is void.
- objectName si:void_state_merge_ok
This method combines
i_error_pop_merge i_loc_pop_rewind/discard i_status_ok
Parsers use it at the end of optional expressions
- objectName si:value_state_merge
This method combines
i_error_pop_merge i_ast_pop_rewind/discard i_loc_pop_rewind/discard
Parsers use it at the end of sequences generating ASTs and choices whose last branch generates an AST
- objectName si:value_notahead_start
This method combines
i_loc_push i_ast_push
Parsers use it at the beginning of negative lookahead predicates which generate ASTs.
- objectName si:void_notahead_exit
This method combines
i_loc_pop_rewind i_status_negate
Parsers use it at the end of void negative lookahead predicates.
- objectName si:value_notahead_exit
This method combines
i_ast_pop_discard/rewind i_loc_pop_rewind i_status_negate
Parsers use it at the end of negative lookahead predicates which generate ASTs.
- objectName si:kleene_abort
This method combines
i_loc_pop_rewind/discard i:fail_return
Parsers use it to stop a positive repetition when its first, required, expression fails.
- objectName si:kleene_close
This method combines
i_error_pop_merge i_loc_pop_rewind/discard i:fail_status_ok i:fail_return
Parsers use it at the end of repetitions.
- objectName si:voidvoid_branch
This method combines
i_error_pop_merge i:ok_loc_pop_discard i:ok_return i_loc_rewind i_error_push
Parsers use it when transiting between branches of a choice when both are void.
- objectName si:voidvalue_branch
This method combines
i_error_pop_merge i:ok_loc_pop_discard i:ok_return i_ast_push i_loc_rewind i_error_push
Parsers use it when transiting between branches of a choice when the failing branch is void, and the next to test generates an AST.
- objectName si:valuevoid_branch
This method combines
i_error_pop_merge i_ast_pop_rewind/discard i:ok_loc_pop_discard i:ok_return i_loc_rewind i_error_push
Parsers use it when transiting between branches of a choice when the failing branch generates an AST, and the next to test is void.
- objectName si:valuevalue_branch
This method combines
i_error_pop_merge i_ast_pop_discard i:ok_loc_pop_discard i:ok_return i_ast_rewind i_loc_rewind i_error_push
Parsers use it when transiting between branches of a choice when both generate ASTs.
- objectName si:voidvoid_part
This method combines
i_error_pop_merge i:fail_loc_pop_rewind i:fail_return i_error_push
Parsers use it when transiting between parts of a sequence and both are void.
- objectName si:voidvalue_part
This method combines
i_error_pop_merge i:fail_loc_pop_rewind i:fail_return i_ast_push i_error_push
Parsers use it when transiting between parts of a sequence and the sucessfully matched part is void, and after it an AST is generated.
- objectName si:valuevalue_part
This method combines
i_error_pop_merge i:fail_ast_pop_rewind i:fail_loc_pop_rewind i:fail_return i_error_push
Parsers use it when transiting between parts of a sequence and both parts generate ASTs.
- objectName si:value_symbol_start symbol
This method combines
if/found? i_symbol_restore $symbol i:found:ok_ast_value_push i:found_return i_loc_push i_ast_push
Parsers use it at the beginning of a nonterminal symbol generating an AST, whose right-hand side may have generated an AST as well.
- objectName si:value_void_symbol_start symbol
This method combines
if/found? i_symbol_restore $symbol i:found:ok_ast_value_push i:found_return i_loc_push i_ast_push
Parsers use it at the beginning of a void nonterminal symbol whose right-hand side may generate an AST.
- objectName si:void_symbol_start symbol
This method combines
if/found? i_symbol_restore $symbol i:found_return i_loc_push i_ast_push
Parsers use it at the beginning of a nonterminal symbol generating an AST whose right-hand side is void.
- objectName si:void_void_symbol_start symbol
This method combines
if/found? i_symbol_restore $symbol i:found_return i_loc_push
Parsers use it at the beginning of a void nonterminal symbol whose right-hand side is void as well.
- objectName si:reduce_symbol_end symbol
This method combines
i_value_clear/reduce $symbol i_symbol_save $symbol i_error_nonterminal $symbol i_ast_pop_rewind i_loc_pop_discard i:ok_ast_value_push
Parsers use it at the end of a non-terminal symbol generating an AST using the AST generated by the right-hand side as child.
- objectName si:void_leaf_symbol_end symbol
This method combines
i_value_clear/leaf $symbol i_symbol_save $symbol i_error_nonterminal $symbol i_loc_pop_discard i:ok_ast_value_push
Parsers use it at the end of a non-terminal symbol generating an AST whose right-hand side is void.
- objectName si:value_leaf_symbol_end symbol
This method combines
i_value_clear/leaf $symbol i_symbol_save $symbol i_error_nonterminal $symbol i_loc_pop_discard i_ast_pop_rewind i:ok_ast_value_push
Parsers use it at the end of a non-terminal symbol generating an AST discarding the AST generated by the right-hand side.
- objectName si:value_clear_symbol_end symbol
This method combines
i_value_clear i_symbol_save $symbol i_error_nonterminal $symbol i_loc_pop_discard i_ast_pop_rewind
Parsers use it at the end of a void non-terminal symbol, discarding the AST generated by the right-hand side.
- objectName si:void_clear_symbol_end symbol
This method combines
i_value_clear i_symbol_save $symbol i_error_nonterminal $symbol i_loc_pop_discard
Parsers use it at the end of a void non-terminal symbol with a void right-hand side.
- objectName si:next_char tok
- objectName si:next_range toks toke
- objectName si:next_alnum
- objectName si:next_alpha
- objectName si:next_ascii
- objectName si:next_ddigit
- objectName si:next_digit
- objectName si:next_graph
- objectName si:next_lower
- objectName si:next_print
- objectName si:next_punct
- objectName si:next_space
- objectName si:next_upper
- objectName si:next_wordchar
- objectName si:next_xdigit
These methods all combine
i_input_next $msg i:fail_return
with the appropriate i_test_xxx instruction. Parsers use them for handling atomic expressions.
Bugs, Ideas, Feedback
This document, and the package it describes, will undoubtedly contain bugs and other problems. Please report such in the category pt of the Tcllib Trackers. Please also report any ideas for enhancements you may have for either package and/or documentation.
When proposing code changes, please provide unified diffs, i.e the output of diff -u.
Note further that attachments are strongly preferred over inlined patches. Attachments can be made by going to the Edit form of the ticket immediately after its creation, and then using the left-most button in the secondary navigation bar.
Keywords
EBNF, LL(k), PEG, TDPL, context-free languages, expression, grammar, matching, parser, parsing expression, parsing expression grammar, push down automaton, recursive descent, state, top-down parsing languages, transducer
Category
Parsing and Grammars
Copyright
Copyright © 2009 Andreas Kupries <andreas_kupries@users.sourceforge.net>

